Create your component file structure
In this section, we go over the different file structures for the component types. The Magento application looks for the files that make up a component including configuration files in particular places inside the component file structure. Follow the predefined file structures for the component type you are developing to ensure that it works as expected.
Root directory location
A component’s root directory is the top-level directory for that component under which its folders and files are located. Depending on how your Magento development environment was installed, your component’s root directory can be located in two places:
-
<Magento install directory>/app: This is the recommended location for component development. You can easily set up this type of environment by Cloning the Magento 2 GitHub repository.- For modules, use
app/code. - For storefront themes, use
app/design/frontend. - For Admin themes, use
app/design/adminhtml. - For language packages, use
app/i18n.
- For modules, use
-
<Magento install directory>/vendor: This location is found in the alternative setups where thecomposer create-projectcommand was used to get a Magento 2 metapackage (which downloads the CE or EE code), or a compressed Magento 2 archive was extracted in order to install Magento.Any third party components (and the Magento application itself) are downloaded and stored under the
vendordirectory. If you are using Git to manage project, this directory is typically added to the.gitignorefile. Therefore, we recommend you do your customization work inapp/code, notvendor.
Required files
The following files are required for all components:
registration.php: Among other things, this file specifies the directory in which the component is installed by vendors in production environments. By default, composer automatically installs components in the<Magento root dir>/vendordirectory. For more information, see Component registration.etc/module.xml: This file specifies basic information about the component such as the components dependencies and its version number. This version number is used to determine schema and data updates whenbin/magento setup:upgradeis run.composer.json: Specifies component dependencies and other metadata. For more information, see Composer integration.
Module file structure
A typical file structure for a Magento 2 module can look like the following:
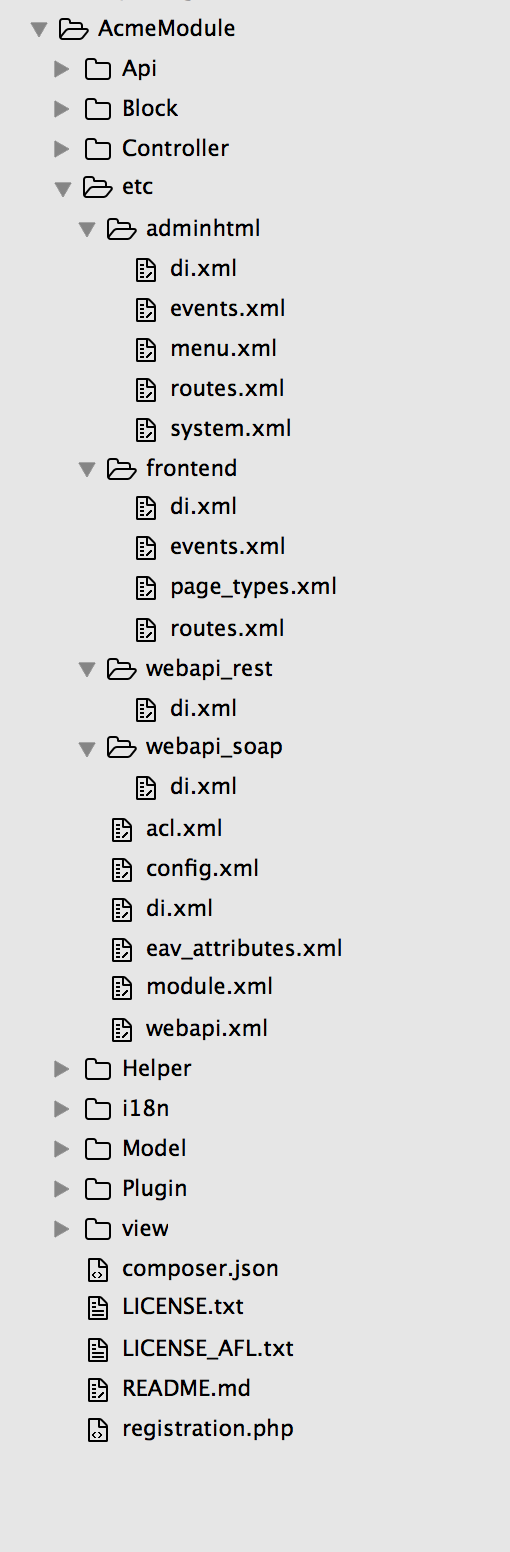
Common directories
Following are some common module directories:
Block: contains PHP view classes as part of Model View Controller(MVC) vertical implementation of module logic.Controller: contains PHP controller classes as part of MVC vertical implementation of module logic.etc: contains configuration files; in particular,module.xml, which is required.Model: contains PHP model classes as part of MVC vertical implementation of module logic.Setup: contains classes for module database structure and data setup which are invoked when installing or upgrading.
Additional directories
Additional folders can be added for configuration and other ancillary functions for items like plugin-ins, localization, and layout files.
Api: contains any PHP classes exposed to the API.i18n: contains localization files.Plugin: contains any needed plug-ins.view: contains view files, including static view files, design templates, email templates, and layout files.
Theme file structure
A typical theme file structure can look like the following:
├── composer.json
├── etc
│ └── view.xml
├── i18n
│ └── en_US.csv
├── LICENSE_AFL.txt
├── LICENSE.txt
├── media
│ └── preview.jpg
├── registration.php
└── web
├── css
│ ├── email.less
│ ├── print.less
│ ├── source
│ │ ├── _actions-toolbar.less
│ │ ├── _breadcrumbs.less
│ │ ├── _buttons.less
│ │ ├── components
│ │ │ └── _modals_extend.less
│ │ ├── _icons.less
│ │ ├── _layout.less
│ │ ├── _theme.less
│ │ ├── _tooltips.less
│ │ ├── _typography.less
│ │ └── _variables.less
│ ├── _styles.less
│ ├── styles-l.less
│ └── styles-m.less
├── images
│ └── logo.svg
└── js
├── navigation-menu.js
├── responsive.js
└── theme.js
Common directories
Typical theme directories are:
etc: Contains configuration files such as theview.xmlfile which contains image configurations for all images and thumbnails.i18n: Translation dictionaries, if any.media: Theme preview images (screen capture of your theme) can be put in here.-
web: Optional directory that contains static files organized into the following subdirectories:css/source: Contains a theme’slessconfiguration files that invoke mixins for global elements from the Magento UI library, and thetheme.lessfile that overrides the default variables values.css/source/lib: Contains view files that override the UI library files stored inlib/web/css/source/lib.fonts: The folder to place the different fonts for your theme.images: Static images folder.js: The folder for your JavaScript files.
For more details on the theme folder structure, see Magento theme structure.
Language package file structure
A typical directory structure for three language packages follows:
├── de_DE
│ ├── composer.json
│ ├── language.xml
│ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt
│ ├── LICENSE.txt
│ └── registration.php
├── en_US
│ ├── composer.json
│ ├── language.xml
│ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt
│ ├── LICENSE.txt
│ └── registration.php
├── pt_BR
│ ├── composer.json
│ ├── language.xml
│ ├── LICENSE_AFL.txt
│ ├── LICENSE.txt
│ └── registration.php
The only required directory for a language package is the top-level directory. Although not required, we recommend that the directory name match the ISO code to identify the locale.
For more information about language packages, see Translation dictionaries and language packages.
Next