Metadata
This topic was updated due to the 2.1.2 MFTF release.
In this topic we talk about handling entities that you need in your tests (such as categories, products, wish lists, and similar) using the MFTF. Using data handling actions like createData, deleteData, updateData, and getData, you are able to create, delete, update, and read entities for your tests. The framework uses two approaches to handle data entities:
You have probably noticed that some modules in acceptance functional tests contain a directory, which is called Metadata .
Example of a module with Metadata
Wishlist
├── Data
├── Metadata
├── Page
├── Section
└── Test
This directory contains XML files with metadata required to handle an entity defined in dataType.
A metadata file contains a list of operations of different type.
Each operation includes:
- The set of adjustments for processing a request in attributes, and in some cases, a response (see
successRegexandreturnRegexin reference details). - The type of body content encoding in contentType.
- The body of the request represented as a tree of objects, arrays, and fields.
When a test step requires handling the specified data entity, the MFTF performs the following steps:
- Reads input data (
<data/>) and the type (thetypeattribute) of the specified entity. - Searches the metadata operation for the
dataTypethat matches entity’stype(for example,<entity type="product">matches<operation dataType="product") . - Forms a request of the operation and the input data of the entity according to matching metadata.
The following diagram demonstrates the XML structure of a metadata file:
Format
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<operations xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../../../../../../vendor/magento/magento2-functional-testing-framework/src/Magento/FunctionalTestingFramework/DataGenerator/etc/dataOperation.xsd">
<operation name=""
dataType=""
type=""
auth=""
url=""
method="">
<contentType></contentType>
<object key="" dataType="">
<field key="">integer</field>
<field key="">string</field>
<field key="">boolean</field>
<array key="">
<value>string</value>
</array>
</object>
</operation>
Principles
- The
dataTypevalue must match thetypevalue of the corresponding entity. - The file name contains data type split with
_and ends with-meta. Example:product_attribute-meta.xml. - A metadata file may contain different types of operations (
type) with the same data entity (dataType). Example:<opeartions> <operation type="create" dataType="category"> ... </operation> <operation type="update" dataType="category"> ... </operation> <operation type="delete" dataType="category"> ... </operation> <operation type="get" dataType="category"> ... </operation> </operations>
Handling entities using REST API
The MFTF allows you to handle basic CRUD operations with an object using Magento REST API requests. Just wrap the corresponding REST API request into XML tags according to the Reference documentation.
GET is used for retrieving data from objects.
POST is used for creating new objects.
PUT is used for updating objects.
DELETE is used for deleting objects.
This is an example of how to handle a category using REST API operations provided by the catalogCategoryRepositoryV1 service.
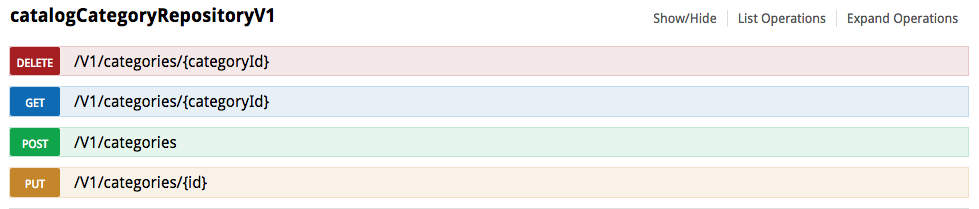
The above screenshot from the Magento REST API Refrence demonstrates a list of available operations to:
- Delete a category by its identifier (
method="DELETE") - Get information about a category by its ID (
method="GET") - Create a new category (
method="POST") - Update category data by its ID (
method="PUT")
We assume that our .env file sets MAGENTO_BASE_URL=https://example.com/ and MAGENTO_BACKEND_NAME=admin.
Create a simple category
Let’s see what happens when you use the <createData entity="_defaultCategory" stepKey="..."/> test step.
The MFTF searches in the Data directory an entity with <entity name="_defaultCategory"> (in case of more than one entity with the same name, all entities are merged) and reads type of the entity.
Catalog/Data/CategoryData.xml
<entity name="_defaultCategory" type="category">
<data key="name" unique="suffix">simpleCategory</data>
<data key="name_lwr" unique="suffix">simplecategory</data>
<data key="is_active">true</data>
</entity>
Here, type is equal to "category", which instructs the MFTF to search an operation with dataType="category".
Since the action is to create a category, the MFTF will also search for operation with type="create" in Metadata for dataType="category".
Catalog/Metadata/category-meta.xml
<operation name="CreateCategory" dataType="category" type="create" auth="adminOauth" url="/V1/categories" method="POST">
<contentType>application/json</contentType>
<object key="category" dataType="category">
<field key="parent_id">integer</field>
<field key="name">string</field>
<field key="is_active">boolean</field>
<field key="position">integer</field>
<field key="level">integer</field>
<field key="children">string</field>
<field key="created_at">string</field>
<field key="updated_at">string</field>
<field key="path">string</field>
<field key="include_in_menu">boolean</field>
<array key="available_sort_by">
<value>string</value>
</array>
<field key="extension_attributes">empty_extension_attribute</field>
<array key="custom_attributes">
<value>custom_attribute</value>
</array>
</object>
</operation>
(The corresponding operation is provided by catalogCategoryRepositoryV1 in REST API.)
The following is encoded in <operation>:
name="CreateCategory"defines a descriptive name of the operation, which is used for merging if needed.dataType="category"defines a relation with data entities with input data for a Category (<entity type="category">).auth="adminOauth"defines Oauth authorization, which is required for the Admin area.url="/V1/categories"defines a routing URL to the corresponding service class. (The request will be sent to https://example.com/rest/V1/categories ifMAGENTO_BASE_URL=https://example.com/andMAGENTO_BACKEND_NAME=adminare set in the acceptance/.env configuration file.)method="POST"defines a POST method of the HTTP request.
<contentType>application/json</contentType> defines a content type of the REST API request, which is set as application/json here.
The parameter that declares a body of the request is catalogCategoryRepositoryV1SavePostBody. Using the Reference, we can trace how the JSON request was converted into XML representation.
Note that comments in the example below are used to demonstrate relation between JSON request and MFTF metadata in XML. JSON does not support comments.
Model schema for catalogCategoryRepositoryV1SavePostBody with XML representation of Catalog/Metadata/category-meta.xml in comments
{ // XML representation in the MFTF metadata format (see 'Catalog/Metadata/category-meta.xml')
"category": { // <object key="category" dataType="category">
"id": 0, // Skipped, because Category ID is not available on UI when you create a new category.
"parent_id": 0, // <field key="parent_id">integer</field>
"name": "string", // <field key="name">string</field>
"is_active": true, // <field key="is_active">boolean</field>
"position": 0, // <field key="position">integer</field>
"level": 0, // <field key="level">integer</field>
"children": "string", // <field key="children">string</field>
"created_at": "string", // <field key="created_at">string</field>
"updated_at": "string", // <field key="updated_at">string</field>
"path": "string", // <field key="path">string</field>
"available_sort_by": [ // <array key="available_sort_by">
"string" // <value>string</value>
], // </array>
"include_in_menu": true, // <field key="include_in_menu">boolean</field>
"extension_attributes": {}, // <field key="extension_attributes">empty_extension_attribute</field>, where 'empty_extension_attribute' is a reference to operation with 'dataType="empty_extension_attribute"' (see 'Catalog/Metadata/empty_extension_attribute-meta.xml')
"custom_attributes": [ // <array key="custom_attributes">
{ // <value>custom_attribute</value>, where 'custom_attribute' is a reference to operation with 'dataType="custom_attribute"' (see 'Catalog/Metadata/custom_attribute-meta.xml')
"attribute_code": "string",
"value": "string"
}
] // </array>
} // </object>
}
So, the body of a REST API request that creates a simple category is the following:
{ // XML representation of input data used to create a simple category ("Catalog/Data/CategoryData.xml")
"category": { // <entity name="_defaultCategory" type="category">
"name": "simpleCategory_0986576456", // <data key="name" unique="suffix">simpleCategory</data>
"is_active": true // <data key="is_active">true</data>
} // </entity>
}
Create an object as a guest
The corresponding test step is:
<createData entity="guestCart" stepKey="..."/>
The MFTF searches in the Data directory an entity with <entity name="guestCart"> and reads type:
Source file: Quote/Data/GuestCartData.xml
<entity name="guestCart" type="guestCart">
</entity>
type="guestCart" points to the operation with dataType=guestCart" and type="create" in the Metadata directory:
Source file: Catalog/Data/CategoryData.xml
<operation name="CreateGuestCart" dataType="guestCart" type="create" auth="anonymous" url="/V1/guest-carts" method="POST">
<contentType>application/json</contentType>
</operation>
As a result, the MFTF sends an unauthorized POST request with an empty body to the https://example.com/rest/V1/guest-carts and stores the single string response that the endpoint returns.
Handling entities using HTML forms
For cases when REST API is not applicable, you may use persisting with HTML forms (when all object parameters are encoded in a URL as key=name attributes).
There are two different attributes to split access to different areas:
auth="adminFormKey"is used for objects in an Admin area.auth="customerFormKey"is used for objects in a store front.
You are able to create assurances with successRegex, and even return values with returnRegex.
Create an object in Admin
The CreateStoreGroup operation is used to persist a store group:
Source file: Store/Metadata/store_group-meta.xml
<operation name="CreateStoreGroup" dataType="group" type="create" auth="adminFormKey" url="/admin/system_store/save" method="POST" successRegex="/messages-message-success/" >
<contentType>application/x-www-form-urlencoded</contentType>
<object dataType="group" key="group">
<field key="group_id">string</field>
<field key="name">string</field>
<field key="code">string</field>
<field key="root_category_id">integer</field>
<field key="website_id">integer</field>
</object>
<field key="store_action">string</field>
<field key="store_type">string</field>
</operation>
The operation is called when <createData> (type="create") points to a data entity of type "group" (dataType="group").
It sends a POST request (method="POST") to http://example.com/admin/system_store/save (url="/admin/system_store/save") that is authorized for the Admin area (auth="adminFormKey").
The request contains HTML form data encoded in the application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type (<contentType>application/x-www-form-urlencoded</contentType>).
If the returned HTML code contains the messages-message-success string, it is resolved as successful.
The operation enables you to assign the following form fields:
group/group_idgroup/namegroup/codegroup/root_category_idgroup/website_idstore_actionstore_type
Create an object in store front
The MFTF uses the CreateWishlist operation to create a wish list on store front:
Source file: Wishlist/Metadata/wishlist-meta.xml
<operation name="CreateWishlist" dataType="wishlist" type="create" auth="customerFormKey" url="/wishlist/index/add/" method="POST" successRegex="" returnRegex="~\/wishlist_id\/(\d*?)\/~" >
<contentType>application/x-www-form-urlencoded</contentType>
<field key="product">integer</field>
<field key="customer_email">string</field>
<field key="customer_password">string</field>
</operation>
The operation is used when <createData> (type="create") points to a data entity of type "wishlist" (dataType="wishlist").
It sends a POST request (method="POST") to http://example.com/wishlist/index/add/ (url="wishlist/index/add/") as a customer (auth="customerFormKey").
The request contains HTML form data encoded in the application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type (<contentType>application/x-www-form-urlencoded</contentType>).
If the returned HTML code contains a string that matches the regular expression ~\/wishlist_id\/(\d*?)\/~, it returns the matching value.
The operation assigns three form fields:
productcustomer_emailcustomer_password
Reference
operations
Root element that points to the corresponding XML Schema.
operation
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string | optional | Name of the operation. |
dataType |
string | required | Data type of the operation. It refers to a type attribute of data entity that will be used as a source of input data. |
type |
Possible values: create, delete, update, get. |
required | Type of operation. |
url |
string | optional | A routing URL of the operation. Example: /V1/categories. The full URL at the end will contain: ENV.baseUrl + /rest/ + url. |
auth |
Possible values: adminOath, adminFormKey, customerFormKey, anonymous |
optional | Type of authorization of the operation. |
method |
string | optional | HTTP method of the operation. Possible values: POST, DELETE, PUT, GET. |
successRegex |
string | optional | Determines if the operation was successful. Parses the HTML body in response and asserts if the value assigned to the successRegex exists. |
returnRegex |
string | optional | Determines if the response contains the matching value to return. |
removeBackend |
boolean | optional | Removes backend name from requested URL. Applicable when auth="adminFormKey". |
GET is used for retrieving data from objects.
POST is used for creating new objects.
PUT is used for updating objects.
DELETE is used for deleting objects.
The following is a list with descriptions the auth possible values:
adminOathis used for REST API persistence in the Admin area with OAuth-based authentication.adminFormKeyis used for HTML form persistence in the Admin area.customerFormKeyis used for HTML form persistence in the Customer area.anonymousis used for REST API persistence without authorization.
contentType
Sets one of the following operation types:
application/jsonis used for REST API operations.application/x-www-form-urlencodedis used for HTML form operations.
object
Representation of a complex entity that may contain fields, arrays, and objects.
An object must match the entity of the same type.
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
key |
string | optional | Name of the object. |
dataType |
string | required | Type of the related entity. |
required |
boolean | optional | Determines if the object is required or not. It must match the Magento REST API specification. |
field
Representation of HTML form or REST API fields.
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
key |
string | required | Name of the field. It must match the field name of the related entity. |
type |
string | optional | Type of the value. It may contain a primitive type or the type of another operation. |
required |
boolean | optional | Determines if the field is required or not. It must match the Magento REST API specification. |
array
Representation of an array.
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
key |
string | required | Name of the array. |
It contains one or more value elements.
value
An item in array.
header
An additional parameter in REST API request.
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
param |
string | required | A REST API header parameter. |
<header param="status">available</header>
param
An additional parameter in URL.
| Attribute | Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
key |
string | required | Name of the URL parameter. |
Example:
<param key="status">someValue</param>