Best practices for store configuration
For detailed information for configuring your store, sites, and websites, you may want to review the Magento 2.2.x User Guide. This page provides best practices, helpful information, and guidelines for configuring your stores, sites, and more with addtional content to post over time and across versions.
Understanding marketing campaigns and promotions
This information is helpful for Magento Commerce (Cloud) 2.1.X and 2.2.X.
To create campaigns and promotions, you will create the options and settings in Content Staging. This feature allows you to create and preview your campaigns prior to making them public for customer sales. The following information provides helpful information. For exact instructions, see the linked Magento 2 User Guide content.
Campaigns are marketing events for seasonal sales, new product lines, and more. Each campaign can include custom themes, blocks for content, widgets to control and display content, and associated promotions with price rules. Due to the extensive nature of a campaign, you create them with a start and end date through Content Staging.
Promotions provide discounts, one time offers, coupons, first time buyer incentives, and more. You create these promotions as Price Rules that set the terms, discounts, and options to encourage customers to buy. You can create price rules on the shopping cart or catalog, with additional options for banners, reward points, and more. We also support scheduling campaigns for your promotions, applying price rules for major events like a new product line or seasonal sales.
The following are tips to help create, update, and manage promotions and campaigns:
- A promotion can be part of a campaign. A campaign cannot be a part of a promotion. You can have lists of promotions as price rules to use multiples times, with multiple campaigns.
- When you create a promotion, it will always create an initial campaign that is inactive. It will have a start date but not an end date. You can ignore this initial campaign. You can Schedule a New Update with the correct campaign schedule and make it active.
- A campaign has a start and end date, not a promotion. The Scheduler that appears when you create a promotion does not configure the start and end dates for the promotion. It allows you so schedule your campaign this promotion is associated with while you are on the promotion’s configuration page.
- You cannot directly edit in Staged Content. If you need to edit settings and options in the campaign, you will need to edit the original or a replica and push to overwrite in Staged Content. For example, if you don’t an end date for a campaign, you must edit the original and push to update.
Advanced Pricing and Staged Content
This information is helpful for Magento Commerce (Cloud) 2.1.X and 2.2.X.
Typically, you can set Advanced Pricing for products through the Products > Catalogs area of the Magento Admin. With Staged Content, you need to complete a few extra steps to add the pricing to a promotion and campaign.
To edit Advanced Pricing and update Content Staging:
- Log into the Magento Admin.
- Navigate to Products > Catalog > and select a product and edit.
- In the Pricing tab, select Advanced Pricing. Edit the price and Save changes.
- At the top of the page, click Schedule New Update.
- Create a new promotion for the product.
- Complete the promotion information. For the Scheduler, enter a begin and end date and time.
- Save the promotion. An inactive initial campaign is created.
- You can Preview to review the special price, promotion name, regular price, and the scheduled date range for the campaign.
For additional steps, you can continue with instructions with Schedule Changes for Catalog Price Rules. Click Next to walk through the steps.
Example Price Rules
Price rules can include logic and conditions as limitless as your marketing imagination. Some popular examples include Buy One Get One Free, Buy One Get One 50% Off, a $25 dollars off on on orders over $100 dollars, and so on.
To create a Price Rule, see our Magento 2 User Guide.
The following provides an example of creating a Price Rule for a First Order Only discount. For this discount, you would want to:
- Create a price rule with a customer segment with a condition: Total Number of Orders less than 1
- Add this customer segment as a condition to the cart rule
- Optional - Add conditions and rules to apply the discounts to specific SKUs or categories of products for focused purchases
This ensures net-new customers or existing customers who have not made a purchase receive the discount only on their very first order. You could create banners and send email promotions for the first time purchase discount.
Understanding websites, stores, and store views
Magento 2 allows you to run multiple stores, websites, with different views all through a single implementation. How they work together to provide multiples stores, sites, catalogs, and shopping experiences can be confusing. This section explains what these are, how they work. To configure a multi-site Magento Commerce (Cloud) implementation, see Set up multiple websites or stores.
You can set up and run several shops through a single implementation of Magento. If you want to have shops that do not interact with each other, you create multiple websites. Each website has specific articles, customer data, checkouts, and shopping cart not shared with other websites in Magento.
Each website can include one or more stores with different categories and articles, with shared customer data, checkout, and shopping cart. For these stores, a customer can sign up once and shop across different catalogs of products with a single checkout.
You can further create store views for different languages, layouts, and designs. Each view can have its own domain, look and feel, and language while sharing articles, customer data, checkout, and shopping cart.
The following are examples to better explain:
-
Single website with one store and two views for Engligh and Spanish locale. All article data, customers, checkout, and shopping cart are shared.
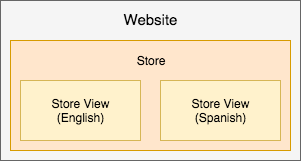
-
Single website with Store A for women’s clothing with two views for English and Spanish, and Store B for children’s clothing with a single store view in English. All article data, customers, checkout, and shopping cart are shared. The stores may have different domains and themes.
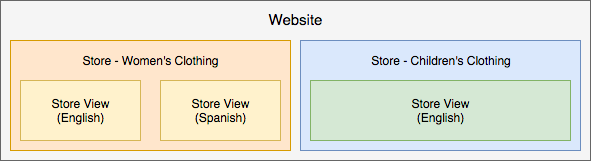
-
Two websites one for clothing and another for home decor with different catalogs and separate articles, customer data, and shopping cart. Each website could have multiple stores and views sharing articles, customer data, checkout, and shopping cart only within that website.
